Sleep is a fascinating and complex biological process that plays a critical role in memory consolidation, emotional processing, and overall well-being. One area of growing interest is how the subconscious mind processes external stimuli, such as affirmations, during different sleep stages. Can playing affirmations while sleeping truly influence thoughts, behaviors, and beliefs?
This article explores the science behind sleep cycles, brain wave activity, and the ideal conditions for subconscious reprogramming. We’ll also provide practical recommendations for optimizing sleep affirmations to achieve the best results.
The Sleep Cycle and Brain Wave Activity
Human sleep consists of several stages that cycle throughout the night in approximately 90–110 minute intervals. These stages are categorized as Non-REM (NREM) sleep and REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep, each with distinct physiological and neurological characteristics.
Brain Waves and Sleep Stages
The brain operates on different frequencies, known as brain waves, that correspond to levels of consciousness and cognitive activity:
- Beta waves (13–30 Hz): Dominant during wakefulness; associated with active thinking and problem-solving.
- Alpha waves (8–12 Hz): Present during relaxation, meditation, and the transition into sleep.
- Theta waves (4–7 Hz): Associated with light sleep, deep relaxation, and high suggestibility—ideal for subconscious programming.
- Delta waves (0.5–4 Hz): Characteristic of deep sleep, where physical restoration occurs and external stimuli are mostly blocked out.
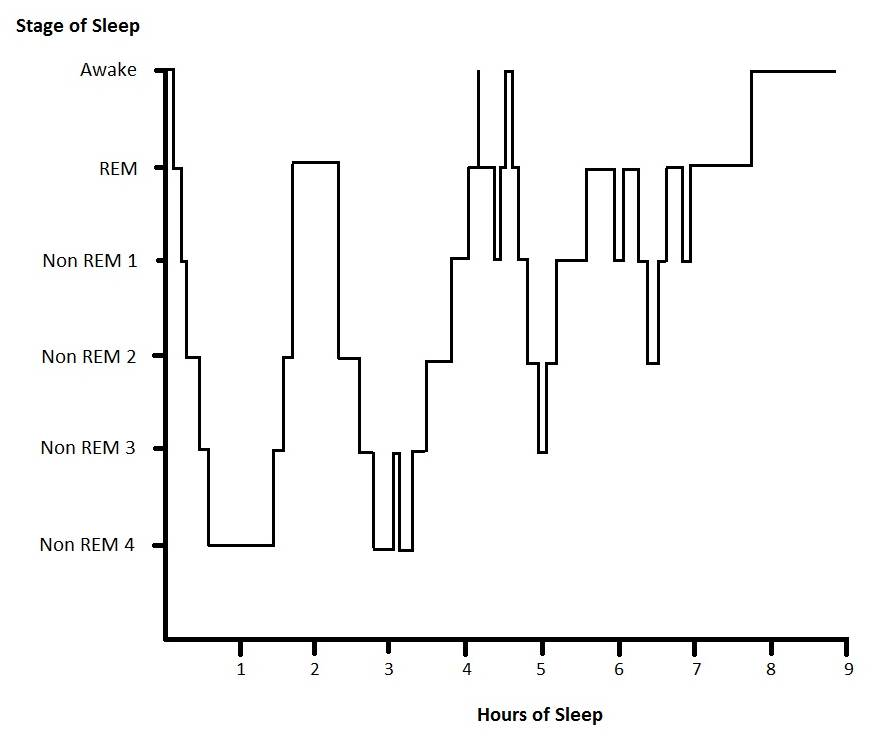
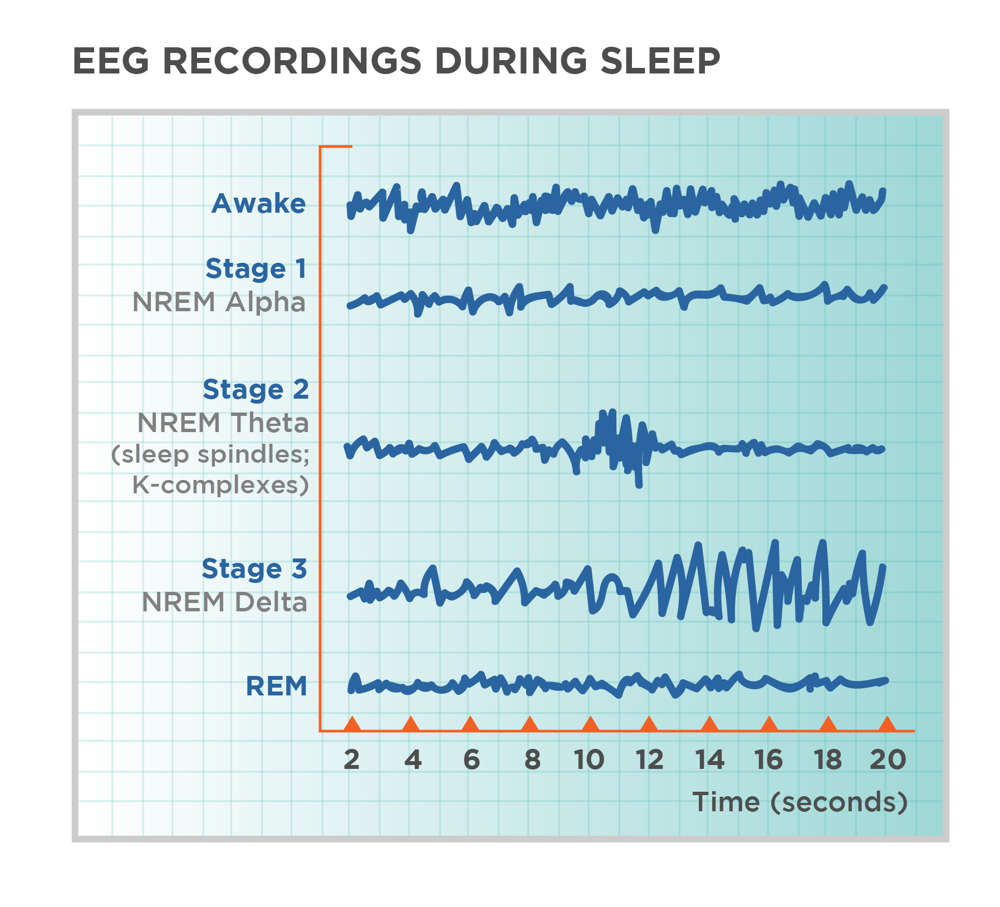
Each sleep stage is defined by its corresponding brain wave activity:
- Stage 1 NREM (Light Sleep / Hypnagogic State)
- Transition from wakefulness to sleep.
- Brain shifts from alpha to theta waves.
- Lasts about 1–7 minutes.
- Highly receptive to external input, making it optimal for subconscious programming.
- Stage 2 NREM (Light Sleep)
- Characterized by sleep spindles (short bursts of brain activity) and K-complexes (high-amplitude waves that help process information).
- Reduces responsiveness to the external environment.
- Lasts 10–25 minutes per cycle.
- Stage 3 NREM (Deep Slow-Wave Sleep – SWS)
- Dominated by delta waves.
- Physical healing, immune system strengthening, and deep relaxation occur.
- Brain is least responsive to external stimuli.
- Lasts 20–40 minutes per cycle, primarily in the first half of the night.
- REM Sleep (Dreaming Stage)
- Brain becomes highly active, resembling wakefulness.
- Memory consolidation, emotional processing, and dreaming occur.
- External sounds may be incorporated into dreams.
- Becomes longer in later sleep cycles, lasting up to an hour.
The Best Time for Affirmations During Sleep
The most receptive state for subconscious programming is the hypnagogic state (Stage 1 NREM) because it features heightened theta wave activity. Research shows that the brain is still processing external stimuli during this stage, making it an ideal window for listening to affirmations.
Studies suggest that:
- Theta waves are associated with deep relaxation and heightened suggestibility.
- During light sleep (Stage 1 and Stage 2), the brain remains partially responsive to external stimuli.
- REM sleep may also play a role in integrating subconscious affirmations into emotions and memories.
Recommendation:
- Start playing affirmations as you are falling asleep to align with the hypnagogic period.
- Use low-volume, repetitive affirmations throughout the night to reinforce subconscious absorption.
- Consider scheduling affirmations to play before waking up during light sleep or REM.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Sleep Affirmations
Several studies highlight how external auditory stimuli can influence memory and behavior during sleep:
- Memory Reactivation in Slow-Wave Sleep:
- A study found that playing a learned melody during deep sleep (Stage 3) enhanced memory recall of that tune upon waking.
- Implication: The brain can strengthen associations during sleep, reinforcing affirmations heard before bedtime.
- Conditioning Behavior During Sleep:
- Researchers paired a negative odor (rotten eggs) with cigarette smoke during sleep.
- Participants had reduced cravings for cigarettes the next day, showing that subconscious learning occurs while asleep.
- Theta Waves and Hypnagogic Learning:
- Brain studies show theta activity is linked to heightened receptivity to new information.
- Children, whose brains naturally have more theta wave activity, absorb language and behaviors more easily.
These findings indicate that sleep, particularly light sleep and early theta-wave phases, can influence thoughts, beliefs, and habits through subconscious exposure.
Practical Tips for Effective Sleep Affirmations
1. Time Affirmations Strategically
- Begin as you are falling asleep to target the hypnagogic state.
- If looping audio, use a fading volume effect to prevent sleep disruption.
- Optionally, schedule affirmations to restart after 4–5 hours (when REM increases).
2. Optimize Volume and Sound
- Keep volume soft and soothing, just audible enough to be registered without waking up.
- Use binaural beats or white noise in the background to enhance relaxation.
- Consider pillow speakers or sleep-friendly headphones for undisturbed listening.
3. Use Repetitive and Positive Phrasing
- Keep affirmations short, simple, and positively framed (e.g., “I am confident and capable” vs. “I will be confident”).
- Repetition strengthens neural pathways, so affirmations should cycle multiple times.
- Use your own voice if possible, as familiarity enhances subconscious absorption.
4. Maintain Consistency
- Listen nightly for at least a few weeks to reinforce subconscious programming.
- Pair sleep affirmations with daytime repetition for maximum impact.
- Track progress in a journal to observe subtle mindset shifts over time.
5. Enhance Your Sleep Environment
- Keep the bedroom dark, cool, and quiet to support sleep quality.
- Avoid blue light exposure (phones/screens) before bed.
- Reduce stimulants (caffeine, heavy meals) before sleep.
Conclusion
The science of sleep affirmations suggests that listening to affirmations during light sleep and theta-dominant phases can enhance subconscious absorption and belief formation. By aligning affirmations with natural brain wave activity, optimizing sound delivery, and maintaining consistency, individuals can effectively reprogram their subconscious mind while they sleep.
If properly structured, sleep affirmations can be a powerful tool for self-transformation, working in harmony with the brain’s nightly process of memory consolidation and subconscious processing. As neuroscience continues to explore the potential of sleep-based learning, affirmations remain a promising, effortless way to nurture positive thoughts and behaviors.